What is Bisphenol? A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Bisphenol and Its Variants
Bisphenol has become a widely discussed chemical in recent years due to its extensive use in everyday products and its potential health impacts. But what exactly is bisphenol? How does it affect human health and the environment? And what about similar compounds like lisphenol? This blog aims to break down everything you need to know about bisphenol and clarify common confusions including “what is lisphenol.”
What is Bisphenol?
Bisphenol refers to a group of chemical compounds that are primarily used to manufacture plastics and resins. The most common type of bisphenol is Bisphenol A (BPA). BPA is an organic synthetic compound widely used in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins.
These plastics and resins are found in many everyday items such as:
-
Water bottles
-
Food containers
-
Canned food linings
-
Thermal paper receipts
-
Medical devices
Bisphenol A has been used since the 1960s and is favored for its durability, clarity, and heat resistance. However, its widespread use has raised concerns because BPA can leach out of products and potentially cause adverse health effects.
The Chemistry Behind Bisphenol
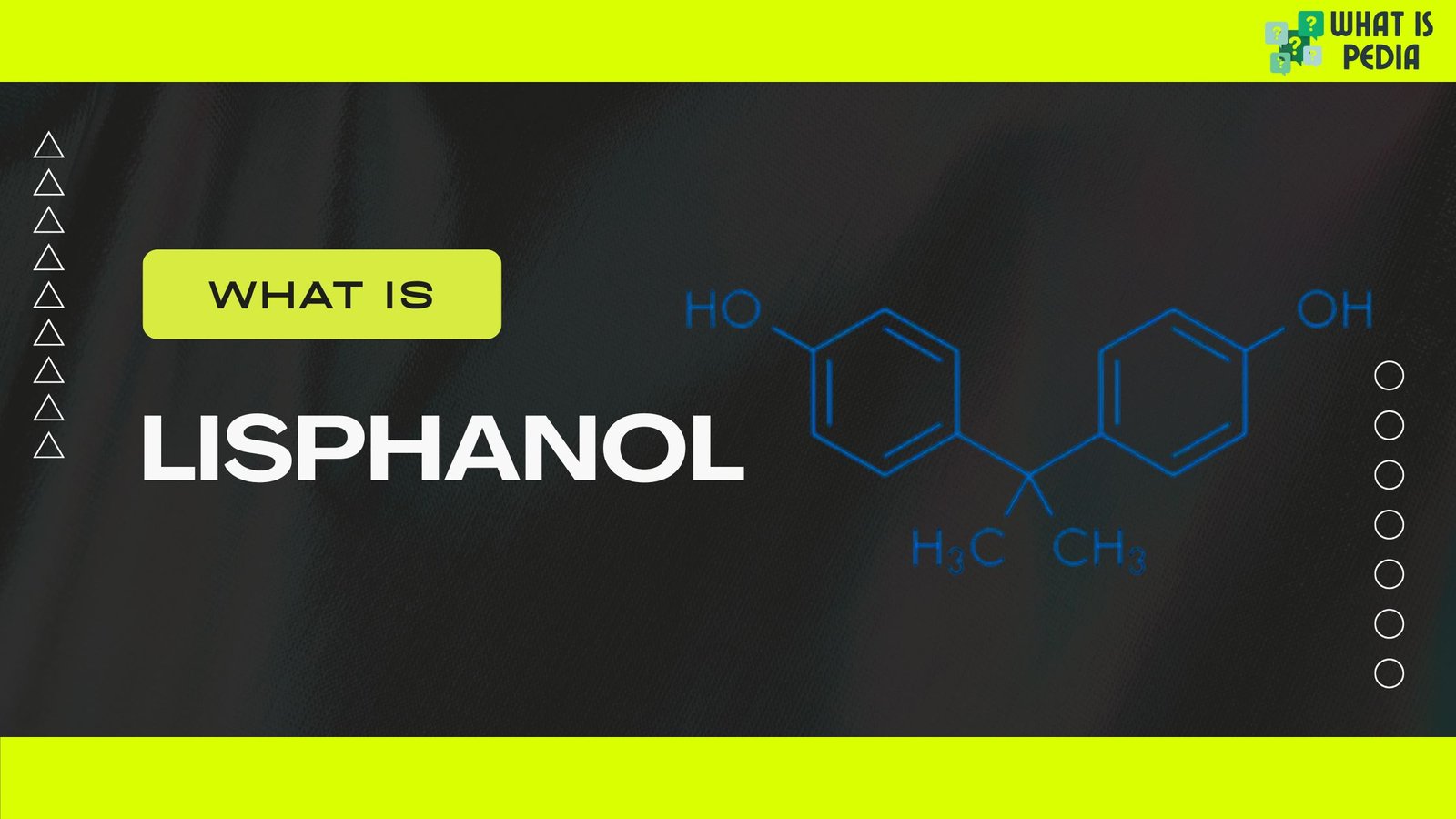
Bisphenols have a basic chemical structure characterized by two hydroxyphenyl groups connected by a bridge of carbon atoms. For BPA, the structure includes two phenol groups connected by a methyl bridge.
Bisphenol A’s chemical formula is C₁₅H₁₆O₂. This structure allows BPA to be used in the synthesis of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins, which are strong, durable, and resistant to heat and impact.
Variants of Bisphenol
While BPA is the most well-known and widely used bisphenol, there are other types as well, including:
-
Bisphenol S (BPS)
-
Bisphenol F (BPF)
-
Bisphenol AP, Bisphenol AF, and others
These variants have similar chemical structures but differ in the bridging groups or substitutions on the phenol rings. Due to concerns over BPA, some manufacturers have replaced BPA with these alternatives, especially BPS and BPF.
What is Lisphenol? Is It Related to Bisphenol?
A common question people search for is “what is lisphenol?” This term sometimes appears in discussions about bisphenols, but it is less well-known and can cause confusion.
Lisphenol is actually not a widely recognized chemical name in scientific literature or industrial use. It might be a typographical or phonetic error or confusion with bisphenol or its variants like bisphenol S (BPS) or bisphenol F (BPF). Sometimes, “lisphenol” may be mentioned mistakenly when people are actually referring to “bisphenol.”
If you are searching for what is lisphenol, chances are you want to know about bisphenol compounds in general or one of their alternatives. For clarity, it’s best to refer to specific bisphenol types like BPA, BPS, or BPF.
Uses of Bisphenol
Bisphenols, especially BPA, are primarily used in the manufacturing sector due to their chemical properties. Some of the most common applications include:
-
Polycarbonate Plastics: Used to make hard, clear plastic products like reusable water bottles, eyeglass lenses, CDs, and medical equipment.
-
Epoxy Resins: Used to coat the inside of metal cans to prevent corrosion and contamination of food and beverages.
-
Thermal Paper: Receipts often contain BPA as a heat-sensitive agent.
-
Dental Sealants and Composites: Some dental materials use BPA derivatives.
-
Electronics and Automotive Parts: Due to their durability and heat resistance.
Health Concerns Associated with Bisphenol
One of the biggest reasons bisphenol compounds have come under scrutiny is their potential health risks. BPA and some of its analogues are classified as endocrine disruptors, which means they can interfere with the body’s hormonal systems.
Potential Health Effects:
-
Hormonal Disruption: BPA can mimic estrogen, a key hormone, potentially causing imbalances in the body.
-
Reproductive Issues: Studies have linked BPA exposure to fertility problems in both males and females.
-
Developmental Problems: Prenatal and early childhood exposure to BPA might affect brain development and behavior.
-
Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Some research suggests BPA exposure may be linked to heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
-
Cancer Risk: Although evidence is not conclusive, BPA exposure is being studied for links to breast and prostate cancers.
Due to these concerns, regulatory agencies around the world have imposed limits on BPA in consumer products, especially those used by infants and children.
Bisphenol Alternatives: Safer or Not?
To reduce the risks associated with BPA, many manufacturers now produce “BPA-free” products that use alternatives like BPS or BPF. However, recent studies suggest that these substitutes might also have similar endocrine-disrupting effects, though research is ongoing.
It’s important to note that the safety profile of bisphenol alternatives is not yet fully understood. Thus, consumers are encouraged to minimize exposure to all bisphenol compounds where possible.
How Does Bisphenol Enter the Human Body?
Bisphenol can enter the human body mainly through:
-
Dietary intake: Leaching from food and beverage containers, especially when heated.
-
Skin contact: Handling thermal paper receipts.
-
Inhalation: Dust contaminated with bisphenols.
Once inside the body, bisphenols are metabolized and excreted fairly quickly. However, frequent and repeated exposure means the body is constantly processing these chemicals.
Reducing Exposure to Bisphenol
Given the potential risks, many people want to know how to reduce their exposure to bisphenols. Here are some practical tips:
-
Avoid plastic containers labeled with recycling codes 3 or 7, which may contain BPA.
-
Use glass, stainless steel, or BPA-free containers, especially for hot foods and drinks.
-
Avoid microwaving food in plastic containers.
-
Minimize handling thermal paper receipts.
-
Choose fresh or frozen foods over canned products when possible.
-
Use safer alternatives for baby bottles and sippy cups.
Environmental Impact of Bisphenol
Bisphenols don’t just affect humans; they also pose environmental risks. Because bisphenol-containing products are widespread, these chemicals can enter soil, water, and air through manufacturing waste and product disposal.
Bisphenols are persistent in the environment and can accumulate in aquatic organisms, potentially disrupting aquatic ecosystems.
Efforts are underway to develop biodegradable alternatives and improve waste management to reduce environmental contamination.
Regulatory Status of Bisphenol
Various countries have taken steps to regulate bisphenol use:
-
The European Union has restricted BPA in baby bottles and is evaluating broader limits.
-
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) prohibits BPA in baby bottles and sippy cups but still allows its use in other food containers with safety limits.
-
Other countries such as Canada, China, and Japan have also imposed restrictions.
Consumers should stay informed about product labels and regulations in their region.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is bisphenol A (BPA)?
Bisphenol A is the most common bisphenol compound used to make plastics and resins. It is known for its durability but also for potential health risks due to its hormonal effects.
2. Is lisphenol the same as bisphenol?
No, lisphenol is not a recognized chemical term. It is likely a misspelling or confusion with bisphenol or one of its variants like bisphenol S or bisphenol F.
3. Are BPA-free products completely safe?
Not necessarily. BPA alternatives such as BPS and BPF may have similar health risks, but research is still ongoing.
4. How can I avoid bisphenol exposure?
Use BPA-free or glass containers, avoid heating plastic, minimize canned foods, and limit handling receipts.
Conclusion
Bisphenol, especially Bisphenol A (BPA), is a widely used chemical essential in many plastic products and coatings. While its usefulness in industry is undeniable, the potential health risks associated with its endocrine-disrupting properties have led to increased scrutiny and regulatory controls.
If you’ve ever searched for “what is lisphenol,” it’s important to clarify that this is not a standard chemical name, and most likely you are referring to bisphenol or one of its related compounds.
By staying informed about bisphenols and making conscious choices about the products we use, we can minimize exposure and promote safer alternatives for our health and the environment.
Learn all about the Academic Performance Indicator (API)—what it is, how it works, and why it matters for students and educators. Read more at whatispedia.in.